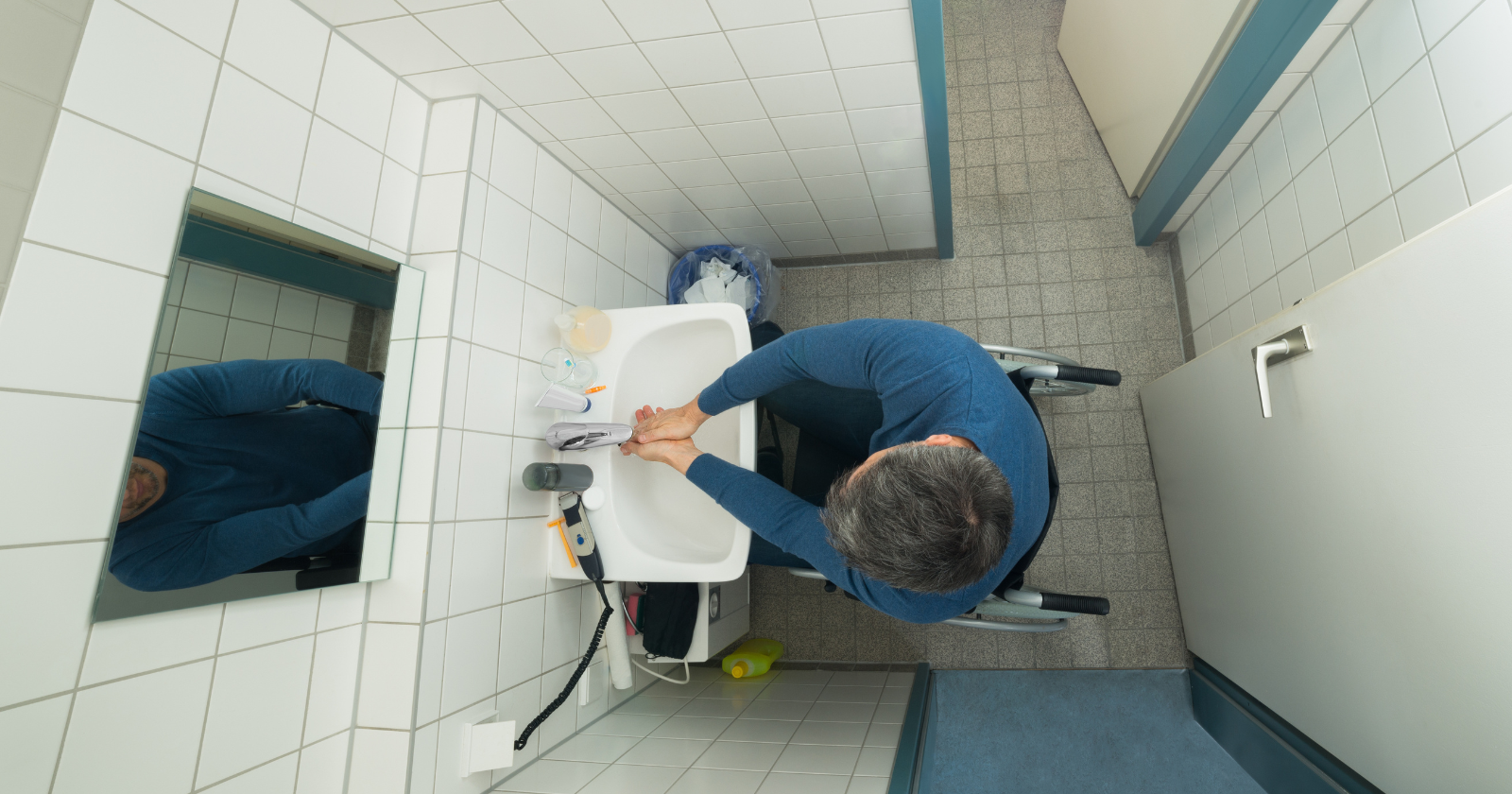
When designing a bathroom for accessibility, the sink is a crucial element to consider. Sinks crafted following the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) guidelines ensure that they are usable by people with disabilities.
These ADA bathroom sinks are designed with features such as appropriate height, knee clearance, and reachable controls to accommodate wheelchair users or those with limited mobility. Not only do these sinks serve a functional purpose, but they also come in a variety of styles to complement the aesthetics of any bathroom space.
To ensure that a bathroom sink is ADA-compliant, it must meet specific requirements. These include dimensions that allow for ease of use from a seated position, faucet designs that are easy to operate, and durable and easy-to-maintain materials.
As part of creating an accessible bathroom, the installation process for an ADA sink must account for the correct placement and clearance. This ensures maximum utility and safety for users with special needs.
Innovations in the design of accessible sinks continue to advance, further improving the usability and comfort of individuals with disabilities.
Key Takeaways
- ADA bathroom sinks are designed to be accessible and functional for individuals with disabilities.
- Compliance with established ADA guidelines is essential in the design and installation of an accessible bathroom sink.
- Maintenance, durability, and advancements in sink accessibility are important factors in the selection of ADA-compliant sinks.
ADA Bathroom Sink Requirements
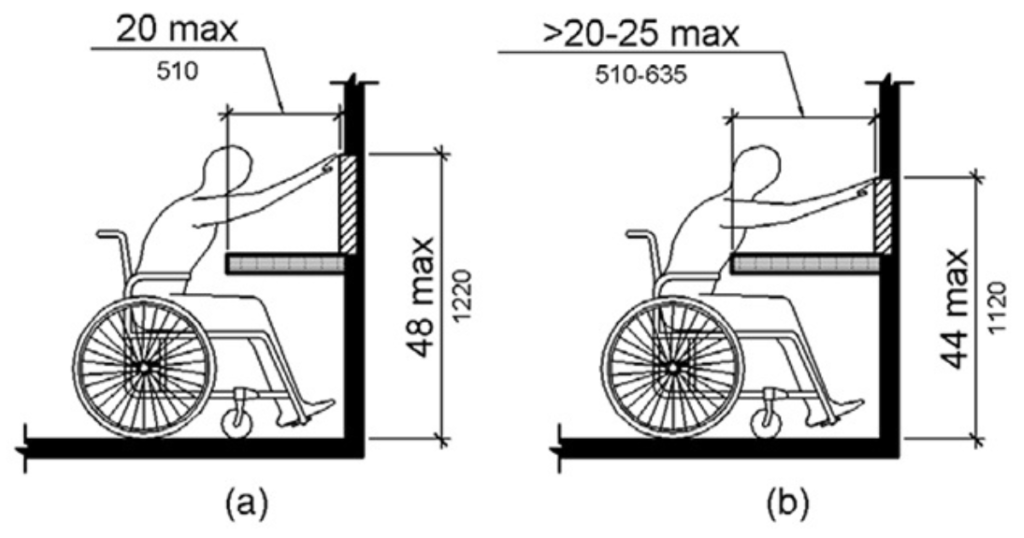
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets forth specific regulations to ensure that bathroom sinks are accessible to individuals with disabilities. These standards aim to accommodate wheelchair users and to provide equal access to bathroom facilities.
Sink Dimensions
ADA regulations stipulate that bathroom sinks must not exceed a height of 34 inches from the floor. This measurement ensures that the sink is reachable for both standing and seated users.
The sink depth should also allow for easy access, meaning that you can access the sink without unnecessary strain.
Clearance Space
Under the sink, there must be a knee clearance of at least 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 11 to 25 inches deep. This space allows a person in a wheelchair to comfortably approach and use the sink without obstruction.
Additionally, there must be enough clear floor space in front of the sink (a minimum of 30 inches by 48 inches) to allow a wheelchair to maneuver.
Faucet Accessibility
Faucets must be operable with one hand and should not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. Lever-operated, push-type, and electronically controlled mechanisms are examples of acceptable faucet designs.
The location of the faucet controls must be within the reachable range for users of all mobility types.
Design Considerations

When designing an ADA-compliant bathroom sink, it’s crucial to prioritize both ergonomic accessibility and aesthetics, ensuring the balance between functionality and design.
Ergonomics
Ergonomically designed ADA bathroom sinks must comply with specific dimensions and clearances to be accessible to individuals with disabilities.
For example, the sink height must not exceed 34 inches from the floor, allowing for easier access by individuals in wheelchairs. Additionally, there must be a knee clearance of at least 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 19 inches deep under the sink.
Faucets should be operable with one hand and should not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist.
See Chapter 6: Lavatories and Sinks from the United States Access Board for more guidelines.
Aesthetics
While meeting accessibility requirements, ADA bathroom sinks can also be aesthetically pleasing, complementing the overall bathroom design.
They come in various styles and materials that cater to different design tastes while maintaining compliance with ADA guidelines.
The sink and fixtures should match the bathroom’s design theme, whether contemporary, traditional, or transitional, without compromising functionality.
For instance, consider the sink’s visual appeal and choose a finish for the fixtures that enhances the bathroom’s appearance, as The Ultimate Guide to Designing an ADA-Compliant Bathroom discusses.
Installation Guidelines
These guidelines will ensure that an ADA bathroom sink is installed in compliance with accessibility standards, providing individuals with disabilities equitable use of bathroom facilities.
Height and Reach Standards
An ADA-compliant bathroom sink must have a maximum rim height of 34 inches from the floor. This ensures that individuals in wheelchairs have appropriate access.
Both the United States Access Board and the ADA Bathroom Requirements emphasize that the sink should allow a minimum knee clearance of 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 19 inches deep from the front edge, underneath the sink.
Drain and Pipe Insulation
Exposed pipes under the sink can be hazardous to individuals with disabilities. The ADA requires pipes and drains to be insulated or otherwise configured to protect against contact. No sharp or abrasive surfaces should be under the sink.
Sink Mounting
When mounting an ADA-compliant sink, the installer must ensure that there is adequate clearance underneath for a wheelchair.
According to US Government ADA Standards, the sink must be mounted with enough wall clearance to maintain a minimum approach area of 30 inches by 48 inches. This clearance must not be obstructed by the door swing or any other bathroom fixture.
Materials and Durability

Durability is a critical factor when selecting materials for an ADA-compliant bathroom sink. These materials must be able to withstand frequent use and heavy wear while maintaining their functionality and aesthetics.
Common materials used include:
- Porcelain: A classic choice, porcelain is noteworthy for its longevity and ease of cleaning. It is often bolstered by a vitreous china coating that provides an additional layer of protection against stains and scratches.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its strength and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel is a practical option that complements a variety of design aesthetics.
- Solid Surface: Materials like acrylic and polyester/resin blends are non-porous, making them resistant to stains and mildew. They can also be repaired if scratched or chipped.
Key considerations for each material include:
- Porcelain: It can chip or crack upon hard impact, though it is generally quite durable.
- Stainless Steel: It can dent and show water spots or fingerprints, requiring regular maintenance.
- Solid Surface: This option is often more easily scratched than the other options, but the scratches can usually be buffed out.
These materials must also be compatible with ADA requirements, including smoothness and temperature-touch response.
They should not become excessively hot or cold to the touch, reducing the risk of injury.
Manufacturers often provide warranties that can give purchasers an indication of the expected lifespan and durability of the sink material.
Proper installation and regular maintenance will also extend the life of the bathroom sink, ensuring it remains functional and accessible for all users.
Compliance and Certification
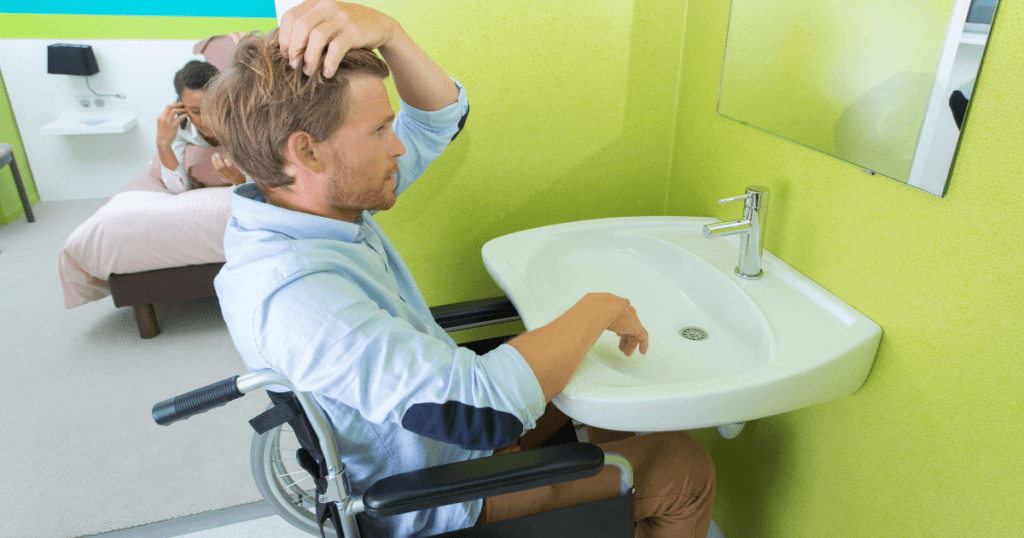

When designing an ADA-compliant bathroom, meeting the sink height and clearance requirements is crucial.
The standard sink height must not exceed 34 inches above the floor, ensuring accessibility for individuals in wheelchairs. Additionally, there must be adequate clearance beneath the sink for knee and toe space, providing a comfortable approach.
Certification involves rigorous inspection to verify that all accessible design standards are met, including the percentage of sinks in accessible spaces that comply with the ADA.
Typically, at least one sink in each ADA-compliant bathroom should offer:
- Clear floor space allows for a forward approach
- Insulation for exposed pipes underneath to prevent potential burns
- Accessible faucet controls that do not require tight grasping or twisting
Beyond individual fixture compliance, the entire bathroom layout is often reviewed for accessible design compliance, ensuring that accessory heights and locations, door hardware, and overall maneuvering space adhere to the standards.
To assure continued compliance, entities may consult with ADA consultants or use the ADA Bathroom Sink Guide for periodic evaluations.
It’s paramount for organizations to stay informed about the ADA standards because adherence not only provides accessibility but also demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity.
Maintenance and Cleaning

Maintaining an ADA-compliant bathroom sink involves regular cleaning and upkeep to ensure it remains accessible and hygienic. Here is a streamlined approach to caring for these fixtures.
Daily Cleaning:
- Surfaces: They should be wiped down with a gentle, non-abrasive cleaner to prevent damage.
- Handles: These need disinfecting to prevent the spread of germs.
Weekly Checks:
- Drainage: Ensure the sink drains properly to avoid water pooling.
- Faucets: Check for leaks and proper operation.
Accessibility Assurance:
- Clear Space: Weekly, one must check that the space below the sink remains clear for knee clearance.
- Pathways: Maintain clear paths to the sink for easy wheelchair access.
Deep Cleaning:
- Descaling: Use a descaling agent to remove any mineral build-up.
- Pipework: Clean the trap to prevent odors and blockages.
Repairs and Replacements:
- Regularly inspect for damages or wear.
- Replace any faulty parts promptly to keep the sink in optimal condition.
An ADA-compliant bathroom sink should meet certain height requirements and have specific dimensions to be accessible. Proper maintenance ensures that these features continue to offer the necessary accessibility and sanitation standards.
Innovations in Accessibility

Recent advancements in ADA bathroom sink design focus on enhancing usability for individuals with disabilities. These improvements, critical for compliance with the 2010 ADA Standards, aim at creating an inclusive environment.
One notable innovation is the introduction of height-adjustable sinks. Users can modify the sink height to cater to their specific needs, helping those in wheelchairs and others with height restrictions.
Hands-free technology is another area of development. Touchless faucets and soap dispensers minimize the need for physical contact, which is not only more hygienic but also eases use for individuals with limited dexterity.
Here is an overview of the enhancements:
- Height-Adjustable Sinks: Allowing for manual or electronic adjustments.
- Hands-Free Technology: Including faucets and dispensers.
- Insulated Pipes: Featured in ADA-compliant restrooms to protect users from potential burns.
Manufacturers such as American Standard are also offering a broader selection of ADA-compliant products. These include sinks with clearance for knee and toe space and protruding objects being minimized for safety.
Purchasing Tips

When selecting an ADA-compliant bathroom sink, consumers should focus on several key requirements to ensure that the product meets accessibility standards.
Height is a critical factor. The sink must be no more than 34 inches above the floor, which is a specification designed to accommodate wheelchair users and individuals of various statures.
Here are some quick guidelines to help with the purchase:
- Height: Ensure the sink is no higher than 34 inches from the floor.
- Knee Clearance: Look for a sink with a minimum knee clearance of 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 11 to 25 inches deep.
- Reach Range: The sink should be within a usable reach range for users, typically within 48 inches from the ground.
| Feature | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Height | Maximum 34 inches |
| Knee Clearance | At least 27″ H x 30″ W x 11-25″ D |
| Reach Range | Within 48 inches |
Additionally, when choosing a sink, buyers should ensure that the area around it is free of any obstructions that could impede access for individuals with disabilities.
This includes considering the space underneath the sink to guarantee proper clearance for wheelchair users’ knees and toes, as outlined in the ADA requirements for sink clearance.
The faucet has to be operable with one hand and should not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist.
It’s advisable to opt for lever-operated, push, touch, or electronically controlled mechanisms that can be used with ease.
Lastly, consumers should remember that ADA-
Compliance also accounts for safety.
Check for the presence of sharp edges or any other design aspects that might pose a risk, particularly to those with mobility or sensory impairments.

Common Challenges and Solutions
When installing ADA-compliant bathroom sinks, one often encounters issues with inadequate clearance.
The ADA mandates a clear space of at least 27 inches from the floor to the bottom of the sink, ensuring that wheelchair users can access the sink comfortably. If a bathroom layout does not allow for this clearance, one solution is to install a wall-mounted sink that removes barriers such as cabinetry.
Another challenge is incorrect sink height.
The sink needs to be mounted with the counter or rim no higher than 34 inches from the floor. Solutions include adjustable height sinks or careful planning during initial construction to meet these specifications.
Improper mirror placement also poses a problem.
The bottom edge of the reflecting surface should be positioned at a height accessible from a seated position. To remedy this, install mirrors that tilt or place them no higher than 40 inches from the top of the floor.
Faucet accessibility is another concern.
Single-handle faucets or those equipped with sensors make usage easier for individuals with limited hand dexterity.
Lastly, the space beneath the sink needs adequate knee clearance – a minimum of 29 inches is required.
If existing cabinetry hinders this, replacing it with open-space designs can resolve the issue.
- Clearance: At least 27 inches of space is required.
- Sink height: Max 34 inches from floor to counter rim.
- Mirror placement: Accessible for seated individuals.
- Faucet type: Single-handle or sensor-activated.
- Knee clearance: Minimum of 29 inches under the sink.
Conclusion

When designing or renovating a bathroom to meet ADA standards, it is critical to prioritize accessibility features for sinks.
The main considerations include ensuring the sink height is not more than 34 inches off the floor and providing knee clearance with at least 27 inches of height, 30 inches in width, and a depth ranging from 11 to 25 inches.
Furthermore, attention should be paid to the sink depth to facilitate ease of use, keeping in mind the requirements for clear floor space.
Adhering to ADA guidelines not only fosters inclusivity but also ensures compliance with legal mandates.
Facilities are advised to consult professionals well-versed in ADA requirements to guarantee that installation is executed properly, integrating these critical spatial considerations:
- Sink Height: Max 34”
- Knee Clearance: 27” H x 30” W
- Depth: 11” – 25”
Compliance with ADA regulations imparts a welcoming environment for people with disabilities and reflects a commitment to accessible design.
It is imperative that these guidelines are regarded as a minimum standard, striving towards an accessible and comfortable bathroom for all users.
What is the rough in height of an ADA sink?
The standard rough-in height for residential bathroom sinks is 31 inches from the floor to the rim of the sink. Bathroom sinks, in compliance with ADA requirements, measure 34 inches from the floor to the rim.
What makes a bathroom sink faucet ADA-compliant?
An ADA-compliant bathroom vanity should be 28 to 34 inches from the floor to the top of the countertop. This specification ensures that the vanity is at a suitable height for an individual in a wheelchair to comfortably roll under it and access the sink.
